DNS Troubleshooting on 4G
Table of Contents
If your 4G device is showing as registered to the network on your sim portal, but you can't get it to connect to www.oemserver.com, there are two likely causes:
- If you are using a custom APN, your APN's firewall settings might need to be adjusted. Please contact your network for help with this.
- If you are using a normal APN with full internet connectivity, the connection might be failing due to a DNS lookup problem.
The DNS problem is most common on recently established NB-IoT networks. When a device first registers on a 4G network, the network sends the device its DNS server details, in a message called the Protocol Configuration Options (PCO). However, on NB-IoT networks, the standard specifies that the new Extended Protocol Configuration Options (ePCO) be used. Many networks have not yet caught up with the standard, and still only support the older PCO message. This must be taken into account when configuring the device's network profile, or it will be unable to connect to the server or download aiding data.
Configuring Your Device for PCO Support
To fix the DNS problem, the 4G network in the device's Admin Parameters must be modified to enable PCO support. Additionally, the device's modem profiles may need to be updated. Since the device won't have network connectivity until this is done, and the profiles cannot be updated over the air, the wired Provisioning Tool must be used.
- Be sure to select 'Set Modem Profiles' in the tool.
- If the network you are using is already present in the networks list, you can simply select it. Otherwise, you must use a custom network string including the 'x' option, as described in this article.
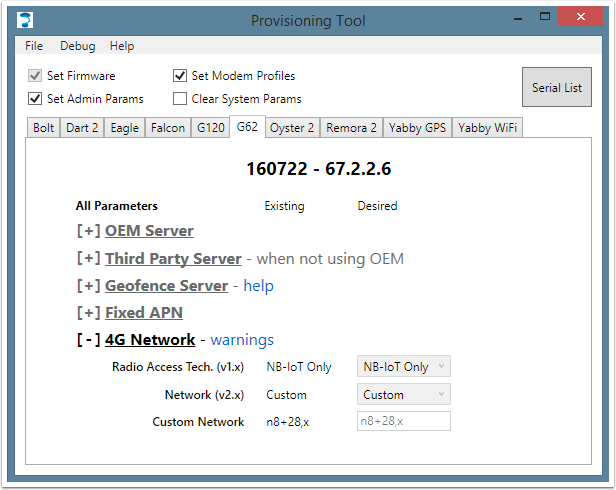
In the example above, a device is configured for NB-IoT on bands 8 and 28, using the PCO to obtain DNS server details.
